Lab File System
- 6 mins1 Large files (moderate)
修改xv6现有的文件系统的inode相关代码,使该文件系统最大能够支持写65803个块。
1.1 原iNode
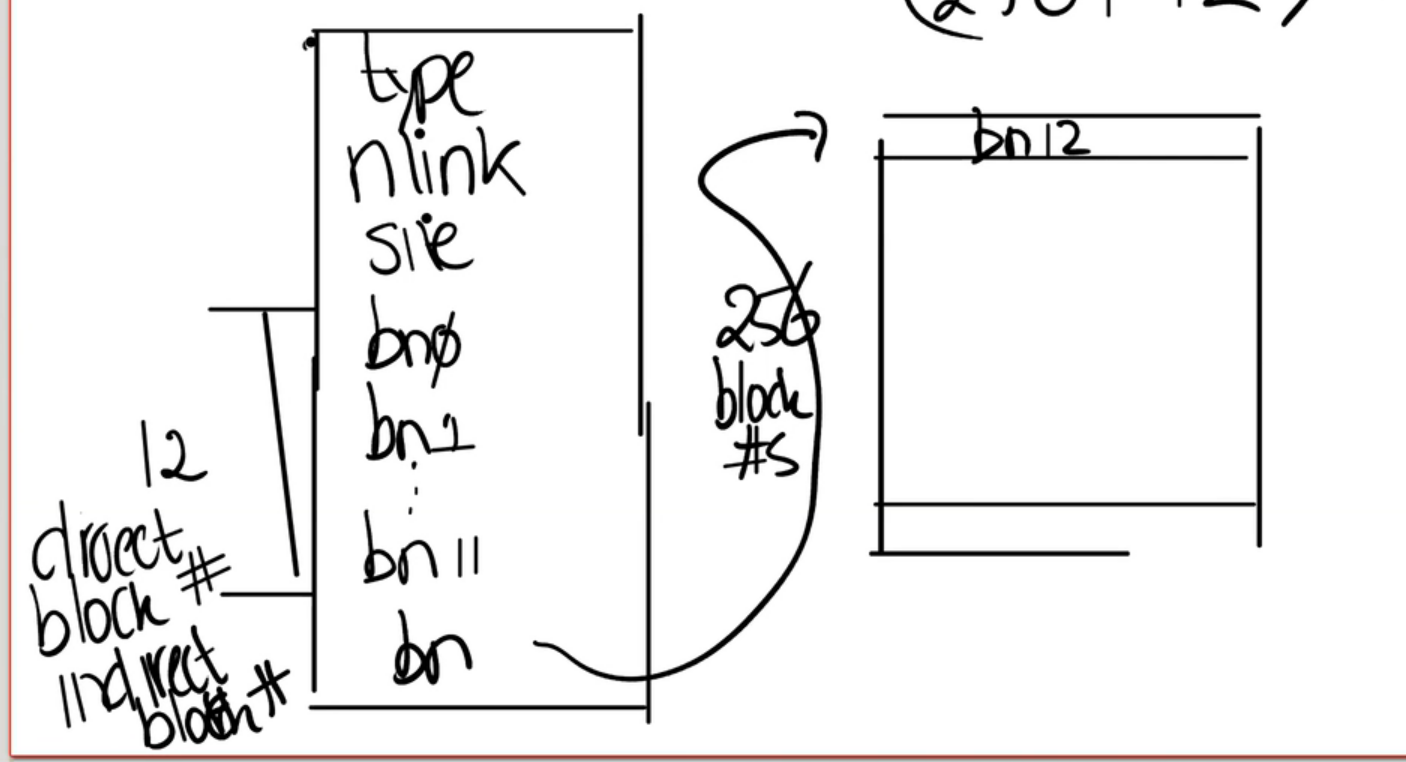
原iNode有12个直接访问块,外加一个间接访问块;而这个间接访问块可以访问256个块。所以原iNode设计可以访问(12+256)个块。而我们现在减少一个直接访问块,增加一个二级间接访问块。一个二级间接访问块,可以访问(256*256)个块。极大的增加了可以访问的块数。
1.3 新iNode
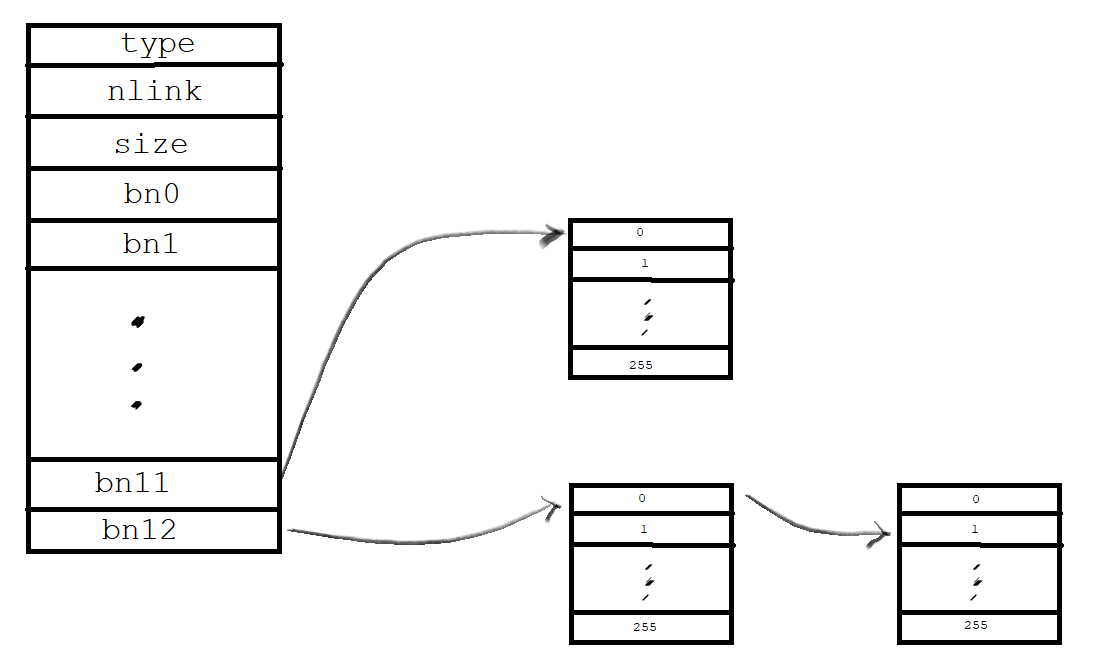
新的iNode相比于原iNode也就是删去了一个直接访问块,增加了一个间接访问块。
1.4 实现新iNode
1.4.1 修改相关宏和结构体
修改直接访问块的数量,增加二级间接访问宏,修改最大文件大小。
#define NDIRECT 11 //direct
#define NINDIRECT (BSIZE / sizeof(uint)) //single direct
#define NDINDIRECT (NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT) //double direct
#define MAXFILE (NDIRECT + NINDIRECT + NDINDIRECT)
修改iNode和dinode结构体的data block addresses的大小:
struct dinode {
short type; // File type
short major; // Major device number (T_DEVICE only)
short minor; // Minor device number (T_DEVICE only)
short nlink; // Number of links to inode in file system
uint size; // Size of file (bytes)
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // Data block addresses
};
struct inode {
uint dev; // Device number
uint inum; // Inode number
int ref; // Reference count
struct sleeplock lock; // protects everything below here
int valid; // inode has been read from disk?
short type; // copy of disk inode
short major;
short minor;
short nlink;
uint size;
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2];
};
1.4.2 修改bmap函数
增加处理二级间接访问即可,可模仿一级间接访问的写法,如果地址不存在,就分配新的块;如果这个新的块被修改,要使用log_write()函数,使之能更新到磁盘中。
部分代码如下:
bn -= NINDIRECT;
if (bn < NDINDIRECT) {
if ((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]) == 0) {
addr = balloc(ip->dev);
if (addr == 0)
return 0;
ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = addr;
}
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if ((addr = a[bn / NINDIRECT]) == 0) {
addr = balloc(ip->dev);
if (addr == 0)
return 0;
a[bn / NINDIRECT] = addr;
log_write(bp);
}
cp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
b = (uint*)cp->data;
if ((addr = b[bn % NINDIRECT]) == 0) {
addr = balloc(ip->dev);
if (addr) {
b[bn % NINDIRECT] = addr;
log_write(cp);
}
}
brelse(cp);
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
1.4.3 修改itrunc函数
增加删除二级间址块的功能,该部分代码也可以仿照一级间址来写。
部分代码如下:
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]) {
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
for (i = 0; i < NINDIRECT; ++i) {
if (a[i]) {
cp = bread(ip->dev, a[i]);
b = (uint *) cp->data;
for (j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; ++j) {
if (b[j])
bfree(ip->dev, b[j]);
}
brelse(cp);
bfree(ip->dev, a[i]);
}
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = 0;
}
然后bigfile测试通过。
2 Symbolic links (moderate)
实现
symlink的系统调用;另一种说法是,使xv6支持软链接(symbolic link)。
symlink在C programmer's manual(RTFM)中描述如下:symlink() creates a symbolic link named linkpath which contains the string target. Symbolic links are interpreted at run time as if the contents of the link had been substituted into the path being followed to find a file or directory. Symbolic links may contain .. path components, which (if used at the start of the link) refer to the parent directories of that in which the link resides. A symbolic link (also known as a soft link) may point to an existing file or to a nonexistent one; the latter case is known as a dangling link. The permissions of a symbolic link are irrelevant; the ownership is ignored when following the link, but is checked when removal or renaming of the link is requested and the link is in a directory with the sticky bit (S_ISVTX) set. If linkpath exists, it will not be overwritten.大致需要这么几点功能:
- 该软链接的名字叫做
linkpath,链接的事物的名字叫做target,这个事物不一定需要存在。(你只需要登记信息就行,登记成功就返回成功信息,登记失败返回失败信息)- 被链接的事物是一个文件或者是一个文件夹
- linkpath不可以重新,也就是调用这个系统调用时,这个linkpath不可以存在。
2.1 实现symlink
2.1.1 检查该系统调用的前提条件
用户是否提供了有效的两个参数,以及这个linkpath是否不存在。如果上述条件不满足,返回错误码-1。
2.1.2 新建iNode
根据实验提供的提示:我们可以将这个软链接保存在一个iNode中,target保存在iiNode的data block中。
你可能会发现ialloc函数可以分配一个iNode节点,但是这个节点不会有数据块,需要用balloc函数分配一个,但是你会发现,balloc函数没法在系统调用函数中使用。
所以通过RTFSC法则发现,sysfile.c中的create函数起到了分配一个iNode的作用,并且返回一个上了锁的iNode。
2.1.3 写入target
当然,你通过create分配到了一个上锁的iNode之后,还是发现这个iNode没有分配数据块,但是你又一次的尝试了使用了balloc分配一个数据块,而且想用bread来读这个数据块。但是,两个问题,第一,balloc函数你还是无法使用;第二,bread返回的buf结构体不知道为啥在系统调用里不能使用了。Compile Error
再次通过RTFSC法则发现,fs.c中的writei函数支持你向iNode中写入信息,而且系统调用可以正常的调用,所以问题解决啦。
看看writei函数:
// Write data to inode.
// Caller must hold ip->lock.
// If user_src==1, then src is a user virtual address;
// otherwise, src is a kernel address.
// Returns the number of bytes successfully written.
// If the return value is less than the requested n,
// there was an error of some kind.
int
writei(struct inode *ip, int user_src, uint64 src, uint off, uint n)
通过这个注释描述,就可以知道这个函数的用法了。off是指在iNode中偏移多少的位置开始写入数据。在这里,我们就希望在偏移量为0,即从头开始写入数据。
2.1.4 代码
uint64
sys_symlink(void)
{
char target[MAXPATH], path[MAXPATH];
struct inode *ip;
if(argstr(0, target, MAXPATH) < 0 || argstr(1, path, MAXPATH) < 0)
return -1;
if (namei(path) != 0) {
return -1;
}
begin_op();
if ((ip = create(path, T_SYMLINK, 0, 0)) == 0) {
end_op();
return -1;
}
if (writei(ip, 0, (uint64)target, 0, MAXPATH) < 0) {
ip->nlink = 0;
iupdate(ip);
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return 0;
}
2.2 修改sys_open
在之前的open系统调用中,并没有支持对inode类型为
T_SYMLINK的支持,修改sys_open,以支持symlink。
2.2.1 O_NOFOLLOW
盲猜,o_nofollow在unix上也有,且也在open调用中使用,于是我们man open来看看文档。
文档中对O_NOFOLLOW的描述如下:
O_NOFOLLOW
If pathname is a symbolic link, then the open fails, with the error ELOOP. Symbolic links in earlier components of the pathname will still be followed. (Note that the
ELOOP error that can occur in this case is indistinguishable from the case where an open fails because there are too many symbolic links found while resolving components
in the prefix part of the pathname.)
This flag is a FreeBSD extension, which was added to Linux in version 2.1.126, and has subsequently been standardized in POSIX.1-2008.
文档中描述的意思是,如果这个标签被设置,则路径是一个软链接的话,就打开错误。
但是在题目中的hints中,该标签的意思是,直接返回这个软链接即可,所以我们只能按照实验的意思写了。
2.2.2 实现O_NOFOLLOW
当系统调用判断了没有创建标记时,且同时打开了路径对应的inode时候(sysfile.c: 335),我们判断该inode是不是一个软链接。如果是软链接,我们进行以下处理:
判断是否有O_NOFOLLOW标记,如果有,直接返回这个软标记。
如果有该标记,打开软链接中target,如果target也是一个软链接,重复该操作,直到链接到一个非软链接的inode。
按照hints,如果软链接到10次,则返回错误
2.2.4 代码
uint64
sys_open(void)
{
char path[MAXPATH];
int fd, omode;
struct file *f;
struct inode *ip;
int n;
argint(1, &omode);
if((n = argstr(0, path, MAXPATH)) < 0)
return -1;
begin_op();
if(omode & O_CREATE){
ip = create(path, T_FILE, 0, 0);
if(ip == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
} else {
if((ip = namei(path)) == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
ilock(ip);
if(ip->type == T_DIR && omode != O_RDONLY){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
// change here
if (ip->type == T_SYMLINK) {
if (!(omode & O_NOFOLLOW)) {
int deep = 0;
while (1) {
deep++;
if (deep == 10) {
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if (readi(ip, 0, (uint64)path, 0, MAXPATH) < 0) {
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
iunlockput(ip);
if ((ip = namei(path)) == 0) {
end_op();
return -1;
}
ilock(ip);
if (ip->type != T_SYMLINK) {
break;
}
}
}
}
// end here
}
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE && (ip->major < 0 || ip->major >= NDEV)){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if((f = filealloc()) == 0 || (fd = fdalloc(f)) < 0){
if(f)
fileclose(f);
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE){
f->type = FD_DEVICE;
f->major = ip->major;
} else {
f->type = FD_INODE;
f->off = 0;
}
f->ip = ip;
f->readable = !(omode & O_WRONLY);
f->writable = (omode & O_WRONLY) || (omode & O_RDWR);
if((omode & O_TRUNC) && ip->type == T_FILE){
itrunc(ip);
}
iunlock(ip);
end_op();
return fd;
}
其实这个实验没有考虑太多的细节,本来想看看编译能不能过,结果直接把测试过了,比较意外。
3 END
意外的结束了实验,测试结果如下:
== Test running bigfile ==
$ make qemu-gdb
running bigfile: OK (133.9s)
== Test running symlinktest ==
$ make qemu-gdb
(0.9s)
== Test symlinktest: symlinks ==
symlinktest: symlinks: OK
== Test symlinktest: concurrent symlinks ==
symlinktest: concurrent symlinks: OK
== Test usertests ==
$ make qemu-gdb
usertests: OK (218.3s)
== Test time ==
time: OK
Score: 100/100
